Augmented Reality system using Planar Homographies.
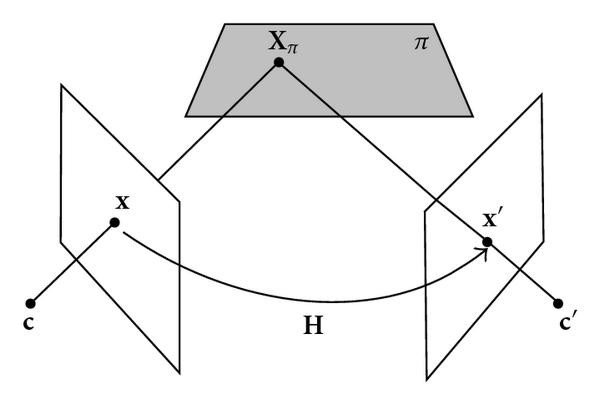 Photo from EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing.
Photo from EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing.MOTIVATION:
Planar homography is a warp operation that maps pixel coordinates from one camera frame to another with the fundamental assumption that the points are lying on a plane in the real world. Under this assumption the mapping can be expressed as x1 ≡ Hx2, where x1 and x2 are homogeneous coordinates and H is the homography matrix.
HOW DOES THE MAPPING WORK?
Before finding the homography matrix between an image pair, we need to find corresponding point pairs between 2 images. We shall use an interest point detector to find particular salient points in the images around which we shall extract feature descriptors. These descriptors try to summarize the content of the image around the feature points in as succinct yet descriptive manner possible.The matching then can be performed by finding the descriptors in either images with the smallest corresponding distance measure ( eg: Euclidean distance). This can be achieved by using FAST detector along with the BRIEF descriptor. We can use these matched points to calculate the Planar Homography matrix that will represent the mapping. The numerical stability of the solution can be improved by normalizing the Homography matrix such that
- Mean of the matrix is now the origin
- The maximum absolute value of the matrix is 1 We can then implement RANSAC to compute a homography. The best homography matrix would be the one with the most inliers found during RANSAC.
See the code and this document https://docs.google.com/document/d/1DErhbBJI4_fr6daAV_Dbo2ECviJ8Sqvarmr163pYWp4/edit?pli=1 to check out the results of the project!